Trial was the first to test a drug meant to delay or halt mental decline in people who have a genetic predisposition
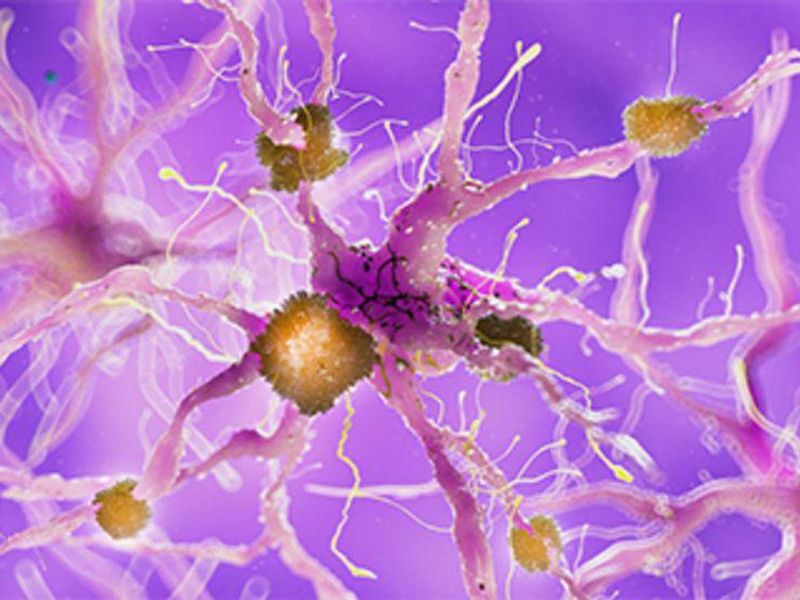
FRIDAY, June 17, 2022 (HealthDay News) — An experimental drug for Alzheimer disease called crenezumab did not prevent or slow mental decline in patients with a genetic mutation that greatly raises the risk for developing the disease, the results of a decade-long clinical trial show.
The mutation, seen in the few hundred study participants from an extended family in Colombia, means they are virtually guaranteed to develop Alzheimer disease in their mid-40s to mid-50s and are highly likely to die in their 60s, The New York Times reported. The trial was the first to test a drug meant to delay or halt mental decline in people who have a genetic predisposition for Alzheimer disease but do not yet have any symptoms.
“We’re disappointed that the treatment did not demonstrate a statistically significant clinical benefit,” Eric Reiman, M.D., executive director of the Banner Alzheimer’s Institute and one of the study leaders, said in a news release announcing the results. “At the same time, we’re proud of the impact that this precedent-setting trial has had in shaping a new era in Alzheimer’s prevention research and we’re extremely grateful to our research participants and their families.”
Crenezumab is a monoclonal antibody from Genenetch, part of the Roche Group. In 2019, Roche halted two other trials of crenezumab in people in the early stages of the more common type of Alzheimer disease because the drug was unlikely to provide any benefits. These latest results add to a series of failures of drugs that target amyloid, The Times reported.
The New York Times Article
Copyright © 2022 HealthDay. All rights reserved.