Childhood diabetes prevention programs should address broader issues of food access and quality, authors say
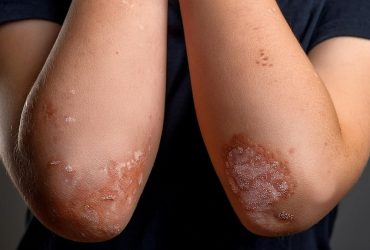
Children experiencing the psychological stress of 'new family structure' in first year of life have increased psoriasis risk
Rates of school disengagement up in 2020, 2021, and 2022 versus 2018, especially for children with mental health conditions
The $50 million in grants will examine how genetics and environment interact
Short sleep duration, increased sleep onset latency, fragmented sleep all tied to self-harm over time
Child-focused screening for MEB problems should start at age 6 months and continue at 12-, 24-, and 36-month health supervision visits
Low adverse childhood experiences and high positive childhood experiences together reduced disordered eating by 20 to 41 percent
Sleep fragmentation negatively linked to physical and social QoL; N2 stage moderates deleterious effects of fragmentation
Link to more depressive symptoms during early adolescence could potentially be due to shorter sleep and worse white matter organization
Associations generally stronger for postnatal than antenatal mental distress